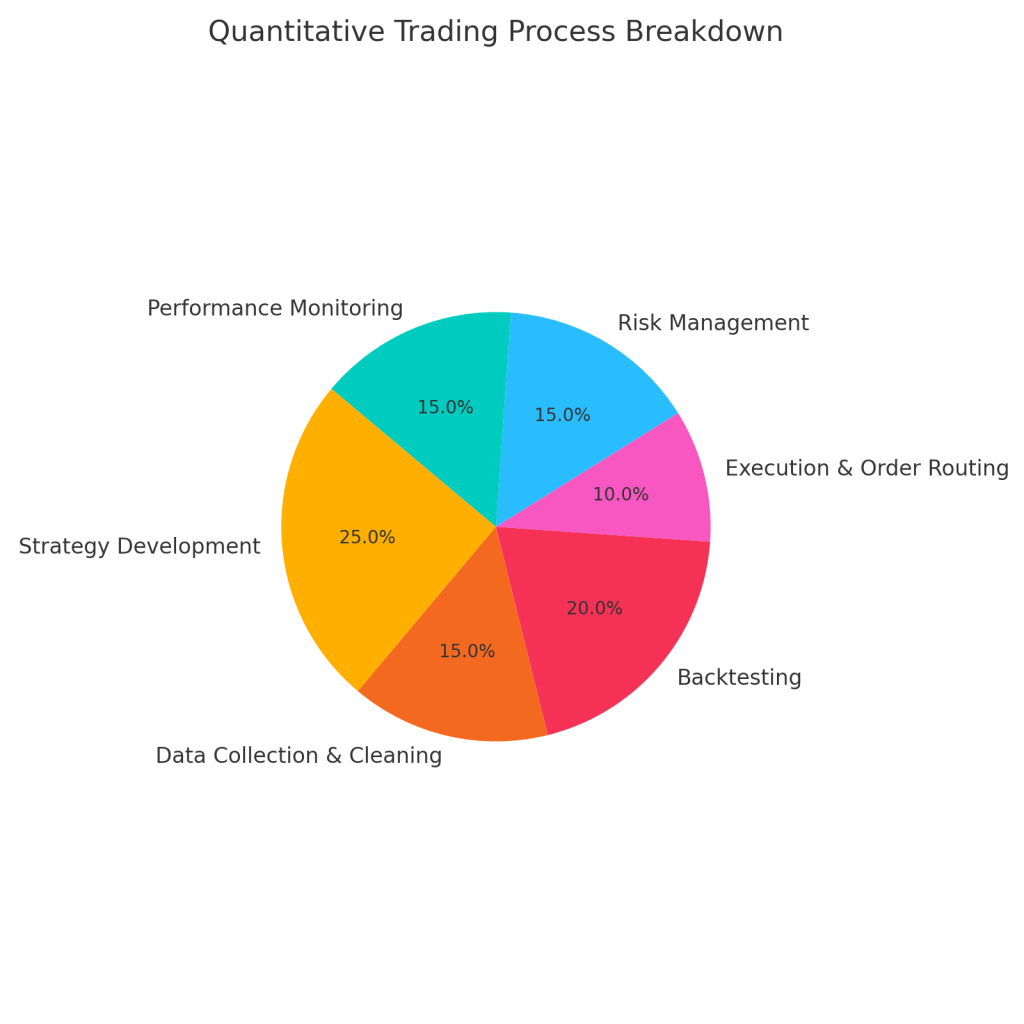
What is Quantitative Trading?
Benefits of Quantitative Trading
Data Collection and Analysis
Model Development
Backtesting and Validation
Strategy 1: Mean Reversion
Description: Assets tend to revert to their historical mean after deviations.
Example:
🔹 Stock XYZ historically averages $50. If price moves significantly above ($55), model signals short; below ($45), model signals long.
Strategy 2: Momentum Trading
Description: Capitalize on persistent price trends.
Example:
🔹 Quant model identifies upward momentum in stock ABC based on price and volume trends; enter long position until momentum weakens.
Description: Employing predictive analytics for trade signals.
Example:
🔹 Use neural networks to analyze extensive historical data, forecasting future price movements with high accuracy.
Step-by-Step Process
Risk Control Techniques
Practical Example:
🔹 Model signals entry with a risk limit of 1% per trade; calculate position size based on volatility and acceptable drawdown limits.
Frequent Mistakes
Solutions
Importance of Discipline
Follow model-driven signals consistently.
Trust the rigor of quantitative methods.
Example 1: Mean Reversion Model
Example 2: Momentum Trading Model
You’ve now explored the foundations of building and implementing robust quantitative trading models. Quantitative trading provides a systematic, disciplined approach that leverages data-driven decisions and rigorous risk management, enabling you to achieve greater consistency and precision in your trading approach.
Sky Links Capital offers advanced resources, professional insights, and continuous support to enhance your trading skills further.
Take your next step today—partner with Sky Links Capital to begin your journey towards trading success!
Risk Warning: Trading in any Financial Instrument is complex and carries a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. It may not be suitable for all investors. Before engaging in any trading activities, you should carefully assess your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and financial situation. If necessary, seek independent financial advice before proceeding with trading.
Sky Links Holding Ltd is a prescribed holding company incorporated in the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), established solely to hold equity interests in financial services subsidiaries. It does not engage in regulated activities or operational control; subsidiaries operate independently under their own regulatory frameworks. The holding company supports capital stability, strategic alignment, and shareholder value across the group.
Sky Links Capital L.L.C. has its registered office located at Offices 208, BB03, Bay Square, Business Bay, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, and is registered with the Dubai Economic Department under License Number 1385407.
Sky Links Capital L.L.C. is a company licensed and regulated by the Securities and Commodities Authority under Category 5, with license number 20200000235. The SCA regulated company, acting as an Introductory firm, in partnership with Sky Links Capital Limited and other renowned regulated entities, is authorized to facilitate services for UAE residents and nationals. Sky Links Capital L.L.C. operates strictly as an Introductory entity and is not authorized to provide investment advice, manage, or hold clients’ assets or money. All services rendered by Sky Links Capital L.L.C. are provided solely on an Introductory basis.
Sky Links Capital Limited is a Limited Company with Investment Dealer (Full Service Dealer excluding Underwriting) under License No. GB24202837 and is authorized and regulated by the Financial Services Commission (FSC) in Mauritius.
Sky Links Capital L.L.C. is a Limited Liability Corporation registered in St Vincent & The Grenadines with registration no. 3698LLC2024.
Sky Links Capital Limited may publish general market commentary from time to time. Sky Links Capital Limited and Sky Links Capital L.L.C. accept no responsibility for any use of the content presented and any consequences of that use. No representation or warranty is given as to the completeness of this information. Anyone acting on the information provided does so at their own risk. The information contained herein is not intended for distribution to residents in any country where such distribution or use would contravene any local law or regulatory requirement. Our products and services are not available to embargoed or sanctioned countries. The information is not intended for distribution to, or use by, any person in any country or jurisdiction where such distribution or use would be contrary to local law or regulation.
Office#208, BB03, Bay Square, Business Bay, Dubai, UAE
+97144957000
Premier Business Center, 10th Floor, Sterling Tower, 14 Poudrière St, Port Louis, Mauritius
+230 5 8282426
Suite 430, Beachmont Business Center, Kingstown, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
+784 5324533
2025 Copyright © Sky Links Capital Limited.